Measuring liquidity in financial markets
Before the global financial crisis GFC , liquidity risk was not on everybody's radar. Financial models routinely omitted liquidity risk. But the GCF has prompted a renewal to understand liquidity risk. One reason is because there was a consensus that the crisis included a run on the shadow non-depository banking system - providers of short-term financing, notably in the repo market - systematically withdrew liquidity ; they did this indirectly but undeniably by increasing collateral haircuts.
After the GFC, all major financial institutions and governments are acutely aware of the risk that liquidity withdrawal can be a nasty accomplice in transmitting shocks through the system or even exacerbating contagion. For more on liquidity, check out Understanding Financial Liquidity.
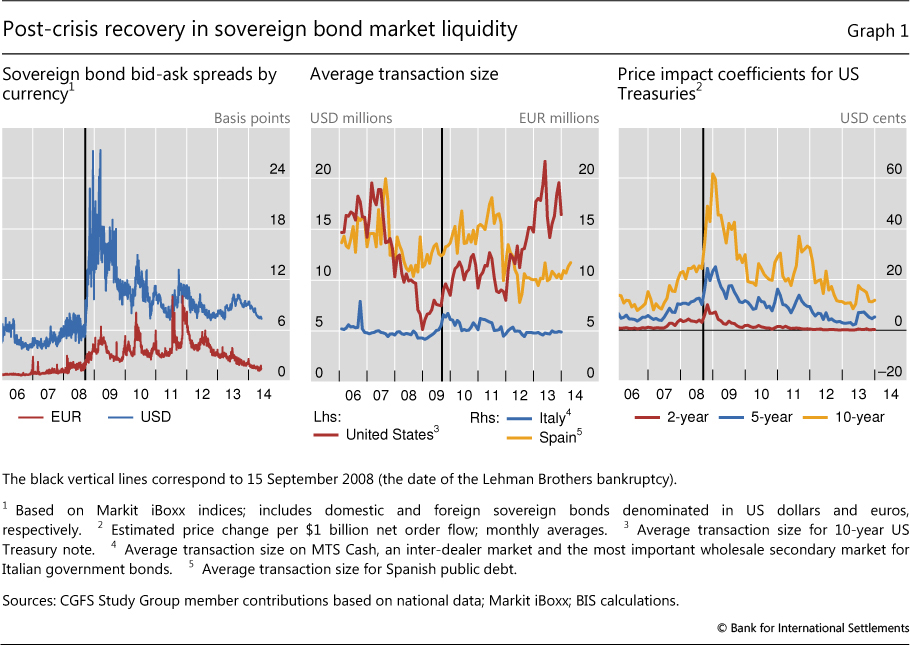
What is liquidity risk? Liquidity risk is divided into two types: Note a common feature of both types of liquidity risk: To learn more about risk, read Determining Risk And The Risk Pyramid. Measures of Market Liquidity Risk There are at least three perspectives on market liquidity see Figure 1. The most popular and crudest measure is the bid-ask spread ; this is also called width. A low or narrow bid-ask spread is said to be "tight" and tends to reflect a more liquid market.
Depth refers to the ability of the market to absorb the sale exit of a position. An individual investor who sells shares of Google, for example, is not likely to impact the share price ; on the other hand, an institutional investor selling a large block of shares in a small capitalization company will probably cause the price to fall.
The 4 Most Important Financial MetricsFinally, resiliency refers to the market's ability to bounce back from temporarily incorrect prices. At one extreme, high market liquidity would be characterized by an owner of a small position relative to a deep market who is exiting into a tight bid-ask spread and a highly resilient market. Trading volume is a popular measure of liquidity, but it is now considered to be a flawed indicator. High trading volume does not necessarily imply high liquidity.
The Flash Crash of May 6, proved this with painful, concrete examples. In that case, according to the SEC , sell algorithms program trades were feeding orders into the system faster than they could be executed. Volume jumped but many backlog orders were not filled.
As the SEC wrote, "especially in times of significant volatility, high trading volume is not necessarily a reliable indicator of market liquidity. A Common Method for Incorporating Liquidity Risk In the case of exogenous liquidity risk, one approach is to use the bid-ask spread to directly adjust the metric. Let's illustrate with value at risk VaR. The position has positive expected return aka drift , but as our horizon is daily we will bring our tiny daily expected return down to zero a common practice.
So let the expected daily return equal zero.

If the returns are normally distributed, then the one-tailed deviate at 5. The full spread represents the cost of a round trip: But, as we are only interested in the liquidity cost if we need to exit sell the position, the liquidity adjustment consists of adding one-half 0.
In the case of VaR, we have: The Bottom Line Liquidity risk can be parsed into funding cash-flow or market asset liquidity risk. Funding liquidity tends to manifest as a credit risk: Market liquidity risk manifests as market risk: Market liquidity risk is a problem created by the interaction of the seller and buyers in the marketplace.
If the seller's position is large relative to the market, this is called endogenous liquidity risk a feature of the seller. If the marketplace has withdrawn buyers, this is called exogenous liquidity risk a characteristic of the market which is a collection of buyers ; a typical indicator here is an abnormally wide bid-ask spread. For more on Value at Risk, see An Introduction To Value at Risk VAR. Dictionary Term Of The Day.
A measure of what it costs an investment company to operate a mutual fund. Latest Videos PeerStreet Offers New Way to Bet on Housing New to Buying Bitcoin?
This Mistake Could Cost You Guides Stock Basics Economics Basics Options Basics Exam Prep Series 7 Exam CFA Level 1 Series 65 Exam. Sophisticated content for financial advisors around investment strategies, industry trends, and advisor education.
Understanding Liquidity Risk By David Harper Share.
Liquidity Measurement Ratios What is liquidity risk? Funding cash flow liquidity risk is the chief concern of a corporate treasurer who asks: A line of credit LOC would be a classic mitigant. Market asset liquidity risk is asset illiquidity. This is an inability to easily exit a position. For example, we may own real estate but, owing to bad market conditions, it can only be sold imminently at a "fire sale" price.
The asset surely has value, but as buyers have temporarily evaporated, the value cannot be realized. Consider its virtual opposite, a U. Treasury bond is considered almost risk-free as few imagine the U.
But additionally, this bond has extremely low liquidity risk: They can be quickly exited at the market price. But positions in many other asset classes , especially in alternative assets , cannot be exited with ease.
In fact, we might even define alternative assets as those with high liquidity risk! Market liquidity risk can be a function of the following: Substitution is the asset fungible?
If a position can be easily replaced with another instrument, the substitution costs are low and the liquidity tends to be higher.
Measuring Treasury Market Liquidity - FEDERAL RESERVE BANK of NEW YORK
If the seller has urgency, this tends to exacerbate the liquidity risk. If a seller is patient, then liquidity risk is less of a threat. Measures of Market Liquidity Measures of Market Liquidity Risk There are at least three perspectives on market liquidity see Figure 1. The bid-ask spread measures liquidity in the price dimension and it is a feature of the market not the seller or the seller's position. Financial models that incorporate bid-ask spread adjust for exogenous liquidity and are exogenous liquidity models.
Position size , relative to the market, is a feature of the seller. Models that use this are measuring liquidity in the quantity dimension and are generally known as endogenous liquidity models.
Resiliency measures liquidity in the time dimensions and such models are currently rare. Learn about the two types of liquidity risk: Liquidity risk is the risk of being unable to sell an asset fast enough to avoid loss.
Understanding how this measure works in the market can help keep your finances afloat. Do your homework, have a long term view, exercise patience, you'll find that investing in small market capitalization stocks is no riskier than investing in large stocks. Professional analysis and constant monitoring of liquidity risk when investing in corporate bonds is highly important.
Learn more about this cheap stock and how its high risk nature, large bid-ask spreads and lack of liquidity may not make it the most wise investment.
Solvency and liquidity are equally important for a company's financial health. Creditors liquidate assets to try and get as much of the money owed to them as possible. The liquidity coverage ratio requires banks and other financial institutions to hold enough cash and liquid assets on hand to weather market stress. Learn how to distinguish between the two broad types of financial liquidity risk: Take a look at the different definitions of liquidity, and find out how investors and businesses attempt to reduce exposure Read about the differences between economic liquidity, financial liquidity and asset liquidity and how each respective type Understand the relationship between a bank's liquid assets and its liquidity and how the financial crisis demonstrated the Learn about what affects an asset's liquidity, including examples of liquid and fixed assets, and how a company's liquidity Learn what a liquid asset is, some examples of liquid assets, what a non-liquid asset is and what determines whether as asset An expense ratio is determined through an annual A hybrid of debt and equity financing that is typically used to finance the expansion of existing companies.
A period of time in which all factors of production and costs are variable.
In the long run, firms are able to adjust all A legal agreement created by the courts between two parties who did not have a previous obligation to each other. A macroeconomic theory to explain the cause-and-effect relationship between rising wages and rising prices, or inflation.
Measuring Liquidity in Financial Markets
A statistical technique used to measure and quantify the level of financial risk within a firm or investment portfolio over No thanks, I prefer not making money. Content Library Articles Terms Videos Guides Slideshows FAQs Calculators Chart Advisor Stock Analysis Stock Simulator FXtrader Exam Prep Quizzer Net Worth Calculator.
Work With Investopedia About Us Advertise With Us Write For Us Contact Us Careers. Get Free Newsletters Newsletters. All Rights Reserved Terms Of Use Privacy Policy.